Privacy risks when logging in other applications with social media accounts
When we install a new app on our mobile device or access a service on a website for the first time we often have to create a user account in order to do so. As an alternative, more services are increasingly offering the possibility of registering using our Google, Apple, Instagram, TikTok, Twitter, Facebook or other social media account allowing us to avoid registering on every website or App we use. While this practice facilitates the ever more exasperating task of managing the credentials of our digital lives, it is not, however, free of certain risks to our privacy.

https://unsplash.com/photos/yyMJNPgQ-X8
To create a new user account in an application or a website it is necessary to provide credentials that are a combination of an identifier (username, email address telephone number or similar) and a password, as well as other registration details. As the number of applications we use increases, the number of credentials we have to manage also grows. This combined with security recommendations that require different strong passwords for each service which we must change frequently means that managing passwords is complicated to such an extent that it's often ignored.
By way of solution to this avalanche of digital identities, a number of different innovations have emerged, including authentication based on federated identity. While this service has been provided for some years, the use of social media credentials to access other service remains a current issue in the security and privacy sectors.
These services are based on an independent third party (e.g. a social media site) which then authenticates the user for the different applications or websites. That means that to access a specific website, we are redirected to a federated authentication service that checks our credentials and, if they’re correct, return the control to the service requested. Furthermore, these authentication services can share essential personal data for registration with the service we want to access so that it’s not necessary to enter data like our name, date of birth, contact details, etc. on another form again.
The ADVANTAGES of these services are:
- They help us reduce the number of credentials we use.
- They make registration processes quicker because many registration details, if not all, are automatically provided by the federated service.
- There is less risk of our credentials being affected by a security breach at the specific service we’re accessing, because these applications and services do not save our passwords in any form. And if they are affected, it would only be necessary to change one password.
Recent years have seen a proliferation of federated identity providers, offered primarily by the major technology companies and social media sites, based on the OAuth standard. Many applications therefore offer the possibility of creating an account and logging into a session directly with your Google, Apple, Twitter, Facebook or other account.
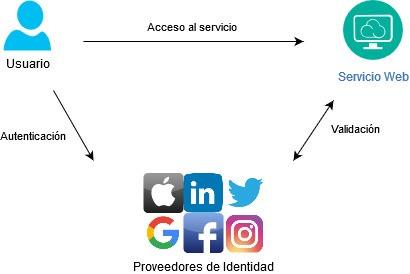
These entities can end up with very complete data on us, our life, our tastes, our hobbies, our interests, etc. thanks to the information we have provided in our user profiles and the data obtained and inferred directly from our use of applications on the internet where we log in using this technique.
The use of federated identity should have adequate guarantees in place to ensure there are no risks such as loss of control over our personal data as they may lead to data flows that end up used for the monitoring or profiling of persons.
Not all federated identity services offer the user the same level of control over the data we share with applications on which we register, nor provide the information in a uniform manner.
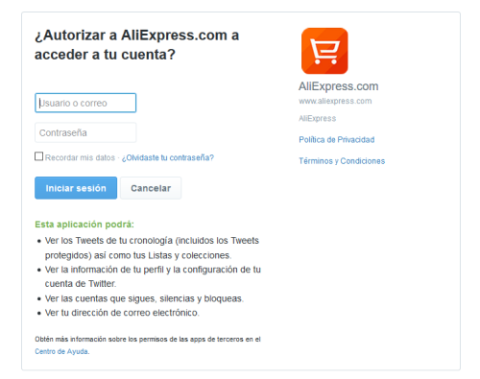
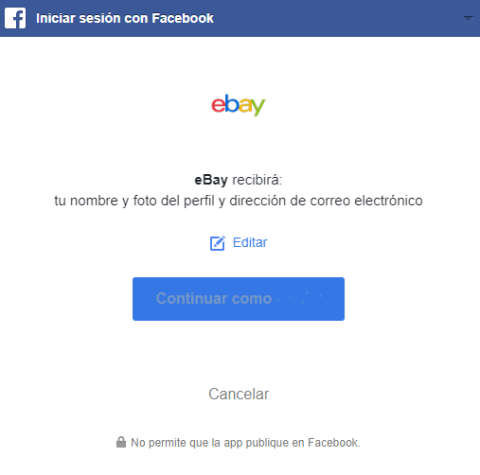
Therefore, the RISKS associated with these technologies include:
- Loss of control of personal data, when the service accesses certain data from the user’s social profile.
- Use of the data obtained from social media for purposes other than those authorised by the user.
- Access of social media to greater information on our use of the applications or online behaviour, facilitating monitoring and profiling.
- In the event of a security breach of the service, the user’s password will not be affected, but much of the information on a user's social profile may be affected, including data on their interests and behavioural advertising profiling data.
- In the event of a loss of control of the social media account (theft of credentials), the user also loses control of the rest of the services where they have registered with this account and they could also be compromised.
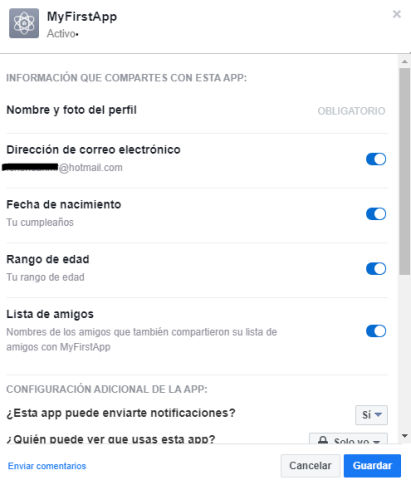
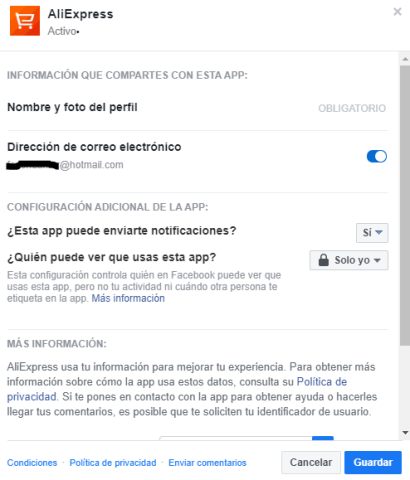
To USE THIS TECHNOLOGY SAFELY, users are advised to follow these recommendations:
- Before logging in to an application using your social media account, inform yourself of this application and the data to which they have access. Consider also the use you are going to make of the application,
- If it's an application you’re not familiar with, that you use only occasionally, or simply something you want to try out, avoid registering using your usual social media credentials. It is recommended that you create a new account for this service or even use federated identity services you have created specifically for accessing services with higher risk.
- Don’t save passwords on the browser or reuse them for different services. Use reliable password managers to generate new, robust passwords, access them when you need them and have them stored safely.
- Use only those federated identity services that offer you the best guarantees with respect to the use of your personal data, greater control of the personal data they’ll share with the application on which you register and the adequate security measures such as a second authentication factor.
- When you use your social media credentials to access an application, make sure that you manage permissions to access your data appropriately, both at the time of registering and subsequently. Avoid allowing them to obtain more data from you than you consider necessary.
- Periodically review the privacy options of your social media account, the applications you have logged into or those you allow login for, deleting or revoking permission for those you have stopped using and manage the personal data that each application can access.
You can find more information on data protection and privacy on the internet on this Agency's Innovation and Technology website and on our blog :


